Methamphetamine Addiction Treatment
What is Methamphetamine?
Methamphetamine is a stimulant drug that is chemically similar to amphetamine (a drug used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy). Regular ‘meth’ is a pill or powder. Crystal meth resembles glass fragments or shiny bluish white “rocks” of various sizes. People can take methamphetamine by smoking, swallowing, snorting, or injecting the drug. Methamphetamine increases the amount of dopamine in the brain, which is involved in movement, motivation, and reinforcement of rewarding behaviors.
What are the Effects of Consuming Methamphetamine?
Short-term health effects include increased wakefulness and physical activity, decreased appetite, and increased blood pressure and body temperature. Long-term health effects include addiction, risk of contracting HIV and hepatitis, severe dental problems ("meth mouth"), intense itching leading to skin sores from scratching, violent behavior, and paranoia. High doses can elevate body temperature to dangerous, sometimes lethal, levels, and cause convulsions and even cardiovascular collapse and death.
Methamphetamine is highly addictive. When people stop taking it, withdrawal symptoms can include anxiety, fatigue, severe depression, psychosis, and intense drug cravings. A person can overdose on methamphetamine and often leads to a stroke, heart attack, or organ problems.
Short-term health effects include increased wakefulness and physical activity, decreased appetite, and increased blood pressure and body temperature. Long-term health effects include addiction, risk of contracting HIV and hepatitis, severe dental problems ("meth mouth"), intense itching leading to skin sores from scratching, violent behavior, and paranoia. High doses can elevate body temperature to dangerous, sometimes lethal, levels, and cause convulsions and even cardiovascular collapse and death.
Methamphetamine is highly addictive. When people stop taking it, withdrawal symptoms can include anxiety, fatigue, severe depression, psychosis, and intense drug cravings. A person can overdose on methamphetamine and often leads to a stroke, heart attack, or organ problems.
Signs and Symptoms
- Dilated pupils
- Accelerated speech
- Paranoia
- Bizarre unpredictable behavior
- Tremors
- Lack of sense of time
- Loss of appetite
- Heavy sweating
- Incoherent speech
- Irritability
- Skin abscesses
- Sleep deprivation
- Dehydration
- Decreased libido
Statistics
774,000
Americans Regularly use Methamphetamine.
964,000
Americans are Addicted to Methamphetamine.
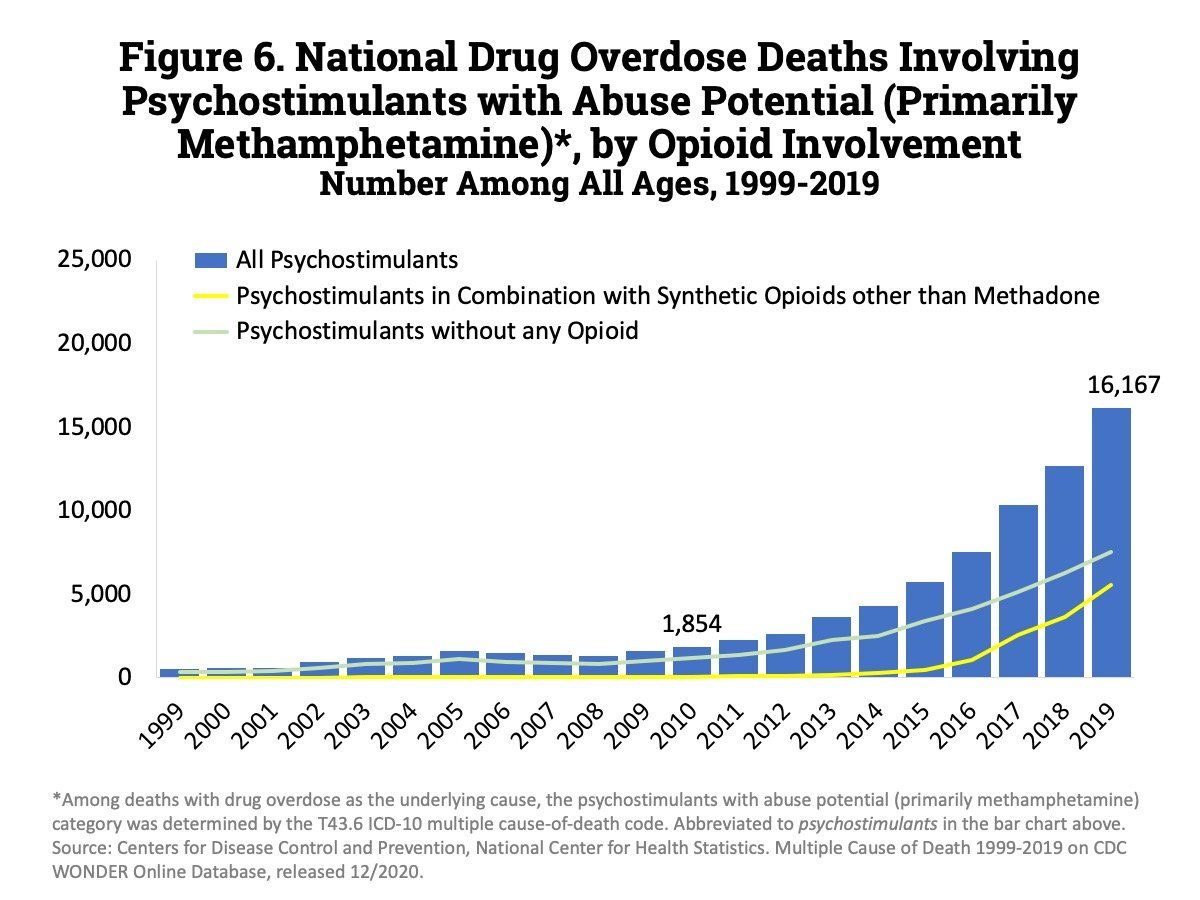
300%
increase in Meth Overdoses from 2011 to 2016.
24
people under the age of 24 who died in 2019 from Fentanyl abuse.
Talk With a Provider Today!
Talk With a Provider Today!
Fighting addiction alone is an almost impossible task. Don't do this alone, call us today to start your road to recovery.